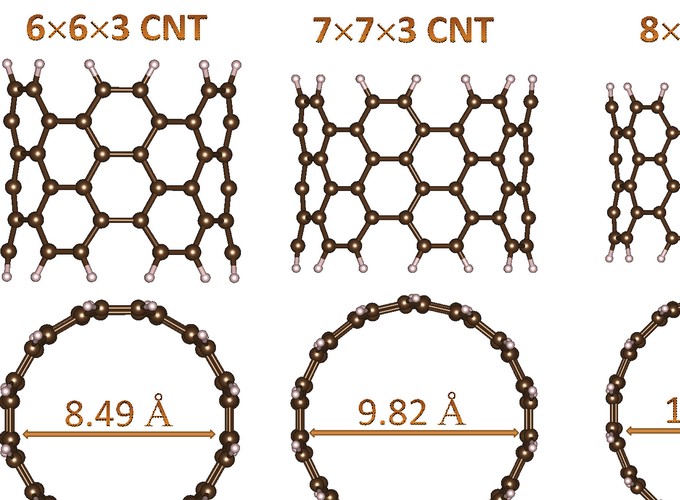
Density functional theory (DFT) is used for investigating the electronic structure and optical properties carbon nanotubes (CNTs) with doped B, Al, Ga, Si, Ge, N, P and As and different diameters. Our results show that the stability of CNTs increased when it comes to an increase in diameter, however, stability decreases depending on doping additives to pure CNTs. B-doped CNTs are the most effective for electronic conductivity due to its lower band gap. The non-linear optical (NLO) properties are discussed according to dipole moment, polarizability, and hyperpolarizability. All the doped CNTs exhibit a good NLO activity. B-, Al-, Ga- and N-doped CNTs have a significant effect on NLO properties. The band gap of CNTs considerably decreased from 2.76 eV to 1.40 eV and 1.78 eV–0.83 eV based on the diameter. The reactivity properties investigated based on chemical hardness, softness, and potential, electronegativity, electrophilicity, the maximum amount of electronic charge index, the electron accepting and donating capability as well as electronic density of states are also presented and analyzed. Herein, the results indicated that the characteristic properties of CNTs can be controlled with different atoms doped CNTs and diameters.